Code coverage for Java - Jacoco
Testing is a very important process in software engineering to ensure the quality of the code we write, and we can ensure testing is adequate by doing code coverage. Code coverage is a process whereby the code coverage software will run through every line of your code, and run your test cases, to determine how much of your code went through the tests and how much didn’t. Then it provides a report, providing this metrics in different levels (packages, classes, etc). You can navigate through the report and find exactly which lines of code are not covered and add test cases for the missed codes.
I’ve already covered the tool for javascripts in the article Code Coverage in Angular. For java, we use Jacoco.
Installing Jacoco for your java code is extremely easy if you are using either gradle or maven, just add the plugin code to your respective build.gradle or pom.xml.
plugins {
id 'jacoco'
}
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
<artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.7.7.201606060606</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>prepare-agent</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>report</id>
<phase>prepare-package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>report</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
Then you should be able to see the tasks - jacocoTestReport and jacocoTestCoverageVerification in the build tool of your IDE. I’m using gradle on intelliJ over here.
However, when you double-click the jacocoTestReport to run it, you might see in your terminal output that it simply skipped the task. That’s because code coverage should run after the testing is run, to determine the coverage. So, to ensure that, add the following lines to your build.gradle.
test {
finalizedBy jacocoTestReport // report is always generated after tests run
}
jacocoTestReport {
dependsOn test // tests are required to run before generating the report
}
The lines above will make the test task a dependency of jacocoTestReport.
Now, double-click the jacocoTestReport and the report will be generated in your build directory - $buildDir/reports/jacoco/test. It looks something like this:
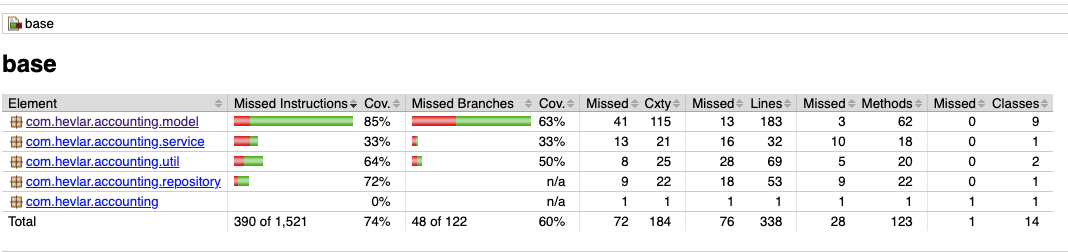
There is another task called jacocoTestCoverageVerification to set a passing score for the code coverage. To implement it, we’ll need to add the following lines to our build.gradle.
jacocoTestCoverageVerification {
violationRules {
rule {
limit {
minimum = 0.9
}
}
rule {
enabled = false
element = 'CLASS'
includes = ['org.gradle.*']
limit {
counter = 'LINE'
value = 'TOTALCOUNT'
maximum = 0.3
}
}
}
}
The above lines specifies that the passing mark should be 0.9, which is 90%. If I run the jacocoTestCodeCoverageVerification on the same code again, I’ll get a failure result.
Execution failed for task ':base:jacocoTestCoverageVerification'.
> Rule violated for bundle base: instructions covered ratio is 0.7, but expected minimum is 0.9
That’s because according to the report I got, my coverage is only 0.7, but the passing score is 0.9. This can be a good way to set some minimum KPI for our projects in order to be deemed of enough quality to publish a release.
